unicycle control for skid steer robotics This work presents a method of utilizing the track or wheel Instantaneous Centers of Rotation (ICRs) on a skid-steer vehicle to map skid-steer dynamics to an equivalent time-varying model . New 2023 KYMRON XH26D Mini Track Excavator. This China excavator has a 26 HP Yanmar diesel engine and features optional Side Swing Boom and Retractable Tracks.
0 · Trajectory tracking control of Skid
1 · The use of unicycle robot control strategies for skid
2 · Path following control of skid
3 · Data
4 · CONTROL OF UNICYCLE TYPE ROBOTS
5 · Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Handling Slip in
China Manufacturer Excavator Hydraulic Cylinder Piston Rod / Ck45 Hard .
While decades of work and hundreds of research papers exist on unicycle robot control, the control of skid-steer robots is not yet as standardized due to the complexity of wheel slipping .This work presents a method of utilizing the track or wheel Instantaneous Centers of Rotation (ICRs) on a skid-steer vehicle to map skid-steer dynamics to an equivalent time-varying model .
skid steer auction australia
A new nonlinear control law for path following with skid-steered mobile robots is proposed, and a kinematic path following control is developed using the Lyapunov approach, . This paper presents algorithms to predict the energy used by a skid‐steer robot to complete a given path, including the refinement of that prediction during operation. skid-steer robots struggle with capturing nonlinear tire-terrain dynamics, especially during high-speed maneuvers. In this paper, we tackle such nonlinearities by enhancing a .
In this paper authors consider the problem of practical stabilization of wheeled mobile robot equipped with skid-steering drive (also know as SSMR). The kinematic model of .
skid steer backhoe attachment canada
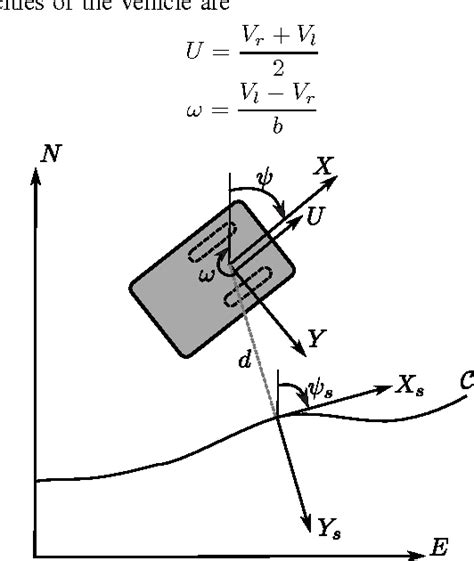
For applications involving differential drive or skid-steer robots, the low-level controller most often leverages a unicycle model, as given in Eq. (1), to drive the robot along the desired path.Abstract: This paper considers the motion control problem of unicycle type mobile robots. We present the mathematical model of the mobile robots taken explicitly into account their . Traditional approaches to motion modeling for skid-steer robots struggle with capturing nonlinear tire-terrain dynamics, especially during high-speed maneuvers. In this . A new nonlinear control law for path following with skid-steered mobile robots is proposed. A terrain dependent kinematic model is utilized in path coordinates, and the .
skid steer auger bit parts
While decades of work and hundreds of research papers exist on unicycle robot control, the control of skid-steer robots is not yet as standardized due to the complexity of wheel slipping behavior. This work presents a method of utilizing the track or wheel Instantaneous Centers of Rotation (ICRs) on a skid-steer vehicle to map skid-steer .
This work presents a method of utilizing the track or wheel Instantaneous Centers of Rotation (ICRs) on a skid-steer vehicle to map skid-steer dynamics to an equivalent time-varying model of unicycle dynamics. A new nonlinear control law for path following with skid-steered mobile robots is proposed, and a kinematic path following control is developed using the Lyapunov approach, taking reachable curvatures and actuator saturation into account. This paper presents algorithms to predict the energy used by a skid‐steer robot to complete a given path, including the refinement of that prediction during operation. skid-steer robots struggle with capturing nonlinear tire-terrain dynamics, especially during high-speed maneuvers. In this paper, we tackle such nonlinearities by enhancing a dynamic unicycle model with Gaussian Process (GP) regression outputs. This enables us to develop an adaptive, uncertainty-informed navigation formulation.
In this paper authors consider the problem of practical stabilization of wheeled mobile robot equipped with skid-steering drive (also know as SSMR). The kinematic model of SSMR is approximated by kinematics of unicycle including small perturbation term which describes limited skidding effect.
For applications involving differential drive or skid-steer robots, the low-level controller most often leverages a unicycle model, as given in Eq. (1), to drive the robot along the desired path.

Abstract: This paper considers the motion control problem of unicycle type mobile robots. We present the mathematical model of the mobile robots taken explicitly into account their dynamics and formulate the respectively motion control strategies of tracking and path-following. Traditional approaches to motion modeling for skid-steer robots struggle with capturing nonlinear tire-terrain dynamics, especially during high-speed maneuvers. In this paper, we tackle such nonlinearities by enhancing a dynamic unicycle model with Gaussian Process (GP) regression outputs.
Trajectory tracking control of Skid
The use of unicycle robot control strategies for skid
A new nonlinear control law for path following with skid-steered mobile robots is proposed. A terrain dependent kinematic model is utilized in path coordinates, and the kinematic parameters are experimentally evaluated. A kinematic path following control is developed using the Lyapunov approach.While decades of work and hundreds of research papers exist on unicycle robot control, the control of skid-steer robots is not yet as standardized due to the complexity of wheel slipping behavior. This work presents a method of utilizing the track or wheel Instantaneous Centers of Rotation (ICRs) on a skid-steer vehicle to map skid-steer .
This work presents a method of utilizing the track or wheel Instantaneous Centers of Rotation (ICRs) on a skid-steer vehicle to map skid-steer dynamics to an equivalent time-varying model of unicycle dynamics.
Path following control of skid
A new nonlinear control law for path following with skid-steered mobile robots is proposed, and a kinematic path following control is developed using the Lyapunov approach, taking reachable curvatures and actuator saturation into account. This paper presents algorithms to predict the energy used by a skid‐steer robot to complete a given path, including the refinement of that prediction during operation. skid-steer robots struggle with capturing nonlinear tire-terrain dynamics, especially during high-speed maneuvers. In this paper, we tackle such nonlinearities by enhancing a dynamic unicycle model with Gaussian Process (GP) regression outputs. This enables us to develop an adaptive, uncertainty-informed navigation formulation.
In this paper authors consider the problem of practical stabilization of wheeled mobile robot equipped with skid-steering drive (also know as SSMR). The kinematic model of SSMR is approximated by kinematics of unicycle including small perturbation term which describes limited skidding effect.
For applications involving differential drive or skid-steer robots, the low-level controller most often leverages a unicycle model, as given in Eq. (1), to drive the robot along the desired path.Abstract: This paper considers the motion control problem of unicycle type mobile robots. We present the mathematical model of the mobile robots taken explicitly into account their dynamics and formulate the respectively motion control strategies of tracking and path-following.
Traditional approaches to motion modeling for skid-steer robots struggle with capturing nonlinear tire-terrain dynamics, especially during high-speed maneuvers. In this paper, we tackle such nonlinearities by enhancing a dynamic unicycle model with Gaussian Process (GP) regression outputs.
skid steer attachments rental illinois
skid steer backup camera systems
Learn how to select a reliable and trustworthy mini excavator manufacturer in China from this ultimate guide. Find out the factors to consider, such as company license, quality certifications, customs data, online sales, website, and customer reviews.
unicycle control for skid steer robotics|The use of unicycle robot control strategies for skid